PHD3 Rabbit mAb[4126]Cat NO.: A81032
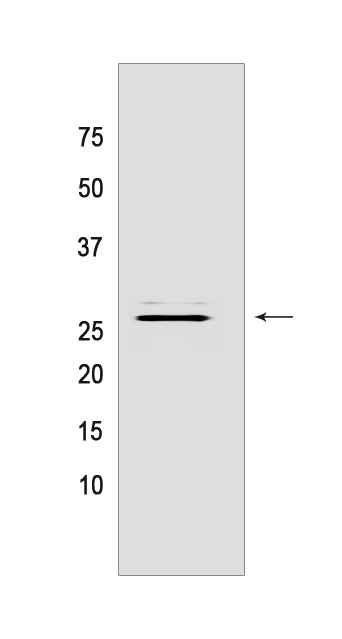
Western blot(SDS PAGE) analysis of extracts from Rat stomach tissue lysate.Using PHD3 Rabbit mAb IgG [4126] at dilution of 1:1000 incubated at 4℃ over night.
Product information
Protein names :EGLN3,EGLN3_HUMAN,Prolyl hydroxylase EGLN3
UniProtID :Q9H6Z9
MASS(da) :27,261
MW(kDa) :27kDa
Form :Liquid
Purification :Protein A purification
Host :Rabbit
Isotype :IgG
sensitivity :Endogenous
Reactivity :Human,Mouse,Rat
- ApplicationDilution
- 免疫印迹(WB)1:1000-2000
- The optimal dilutions should be determined by the end user
Specificity :Antibody is produced by immunizing animals with a synthetic peptide of human PHD3.
Storage :Antibody store in 10 mM PBS, 0.5mg/ml BSA, 50% glycerol. Shipped at 4°C. Store at-20°C or -80°C. Products are valid for one natural year of receipt.Avoid repeated freeze / thaw cycles.
WB Positive detected :Rat stomach tissue lysate
Function : Prolyl hydroxylase that mediates hydroxylation of proline residues in target proteins, such as PKM, TELO2, ATF4 and HIF1A (PubMed:19584355, PubMed:21620138, PubMed:21483450, PubMed:22797300, PubMed:20978507, PubMed:21575608). Target proteins are preferentially recognized via a LXXLAP motif. Cellular oxygen sensor that catalyzes, under normoxic conditions, the post-translational formation of 4-hydroxyproline in hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) alpha proteins (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Hydroxylates a specific proline found in each of the oxygen-dependent degradation (ODD) domains (N-terminal, NODD, and C-terminal, CODD) of HIF1A (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Also hydroxylates HIF2A (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Has a preference for the CODD site for both HIF1A and HIF2A (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Hydroxylation on the NODD site by EGLN3 appears to require prior hydroxylation on the CODD site (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Hydroxylated HIFs are then targeted for proteasomal degradation via the von Hippel-Lindau ubiquitination complex (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). Under hypoxic conditions, the hydroxylation reaction is attenuated allowing HIFs to escape degradation resulting in their translocation to the nucleus, heterodimerization with HIF1B, and increased expression of hypoxy-inducible genes (PubMed:11595184, PubMed:12181324). ELGN3 is the most important isozyme in limiting physiological activation of HIFs (particularly HIF2A) in hypoxia. Also hydroxylates PKM in hypoxia, limiting glycolysis (PubMed:21620138, PubMed:21483450). Under normoxia, hydroxylates and regulates the stability of ADRB2 (PubMed:19584355). Regulator of cardiomyocyte and neuronal apoptosis. In cardiomyocytes, inhibits the anti-apoptotic effect of BCL2 by disrupting the BAX-BCL2 complex (PubMed:20849813). In neurons, has a NGF-induced proapoptotic effect, probably through regulating CASP3 activity (PubMed:16098468). Also essential for hypoxic regulation of neutrophilic inflammation (PubMed:21317538). Plays a crucial role in DNA damage response (DDR) by hydroxylating TELO2, promoting its interaction with ATR which is required for activation of the ATR/CHK1/p53 pathway (PubMed:22797300). Also mediates hydroxylation of ATF4, leading to decreased protein stability of ATF4 (Probable)..
Tissue specificity :Widely expressed at low levels. Expressed at higher levels in adult heart (cardiac myocytes, aortic endothelial cells and coronary artery smooth muscle), lung and placenta, and in fetal spleen, heart and skeletal muscle. Also expressed in pancreas. Localized to pancreatic acini and islet cells..
Subcellular locationi :Nucleus. Cytoplasm.
IMPORTANT: For western blots, incubate membrane with diluted primary antibody in 1% w/v BSA, 1X TBST at 4°C overnight.